Exploring the World of Operating Systems: An Overview of Types and Their Roles
Introduction
In the vast landscape of computing, an operating system (OS) serves as the backbone that enables computers and devices to function efficiently and interact with users. An operating system acts as an intermediary between hardware and software, managing resources, providing user interfaces, and facilitating seamless communication. In this blog, we will delve into the fascinating world of operating systems, exploring their types and the critical roles they play in modern technology.

What is an Operating System?
An operating system is a software program that manages computer hardware and software resources and provides services for computer programs. It serves as a crucial link between applications and hardware components, allowing software to interact with the underlying system and utilize resources such as memory, storage, and processing power effectively.
Types of Operating Systems
There are several types of operating systems, each designed for specific purposes and platforms. Let's explore the most common types:
Single-User, Single-Tasking OS
This type of OS is designed for individual users and can handle only one task at a time. Early operating systems, like MS-DOS (Microsoft Disk Operating System), are examples of single-user, single-tasking systems.
Single-User, Multi-Tasking OS
These operating systems allow a single user to run multiple applications simultaneously. They efficiently manage resources and use time-sharing techniques to switch between tasks quickly. Popular examples include Microsoft Windows and macOS.
Multi-User OS
Multi-user operating systems support multiple users simultaneously, each with their individual accounts. These OS types offer robust security features to protect data and maintain user isolation. Unix-based systems, like Linux and FreeBSD, are prime examples of multi-user operating systems.
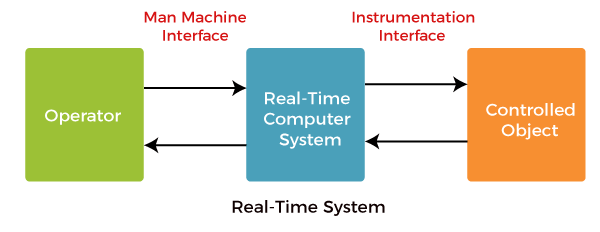
Real-Time OS (RTOS)
RTOS is designed for systems that require real-time processing, where tasks must be completed within strict time constraints. RTOS is commonly used in robotics, industrial automation, and aerospace applications.
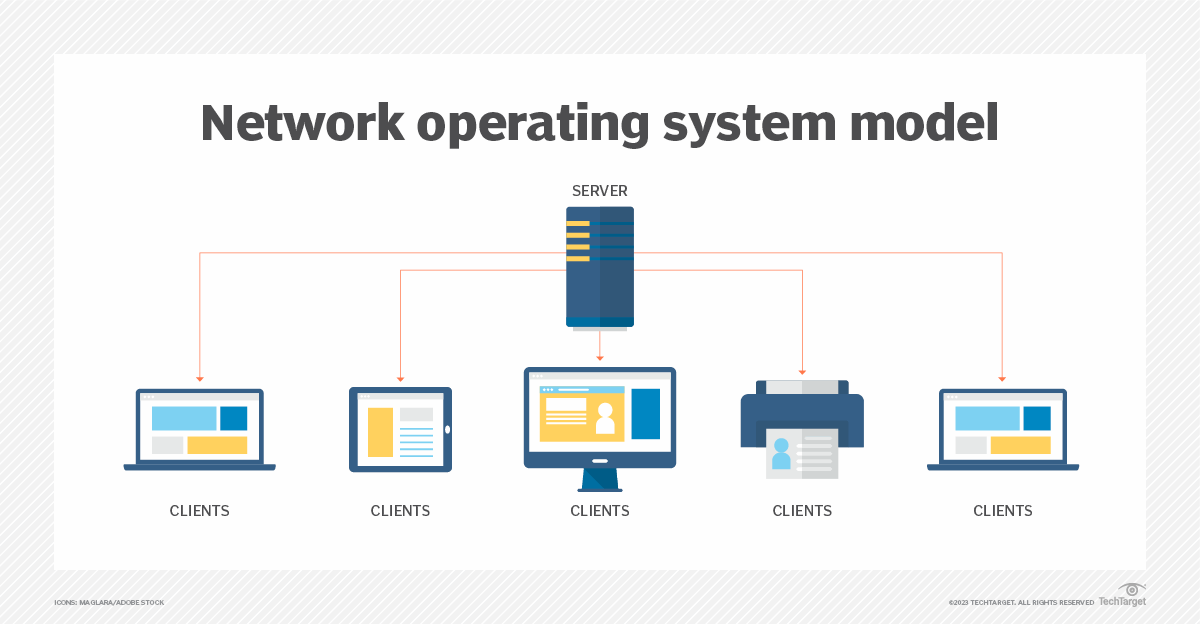
Network OS
A network operating system enables multiple computers to communicate and share resources across a network. These systems facilitate tasks like file sharing, printer management, and centralized user administration. Novell NetWare and Windows Server are popular examples of network operating systems.
Embedded OS
Embedded operating systems are designed for specialized devices like smartphones, IoT devices, and embedded systems. They are compact, efficient, and often customized to meet the requirements of the specific device.
The Role of Operating Systems
Operating systems play several essential roles in the world of computing:
Resource Management: OS manages computer resources, including CPU scheduling, memory allocation, and peripheral devices. It ensures fair distribution of resources among different applications and users.
User Interface: Operating systems provide user interfaces that allow users to interact with the computer. Graphical User Interfaces (GUIs) have become prevalent, offering intuitive and visually appealing ways to navigate the system.
File Management: The OS handles file storage and organization on disks. It creates, reads, writes, and deletes files, ensuring data is stored efficiently and securely.
Security: Operating systems implement security mechanisms to protect against unauthorized access, malware, and other threats. User accounts, permissions, and encryption are some of the security features they offer.
Device Management: OS facilitates communication between hardware devices and software applications. It includes drivers that enable devices to function correctly and efficiently.
Error Handling: Operating systems are responsible for error handling and recovery. When an application encounters an error, the OS attempts to resolve it gracefully and prevent system crashes.
Conclusion
Operating systems are the unsung heroes of modern computing, working behind the scenes to ensure our devices run smoothly and efficiently. From managing resources to providing user interfaces and ensuring security, they perform a myriad of critical tasks. Understanding the different types of operating systems helps us appreciate their diverse roles in powering the technology that surrounds us.
As technology continues to advance, operating systems will evolve, adapting to new challenges and opportunities. Whether we interact with computers, smartphones, or smart home devices, operating systems will remain the cornerstone of our digital experiences.

